The Future of Privacy Forum on Tuesday released a framework for regulating biometric data for immersive technologies.
FPF’s Risk Framework for Body-related Data in Immersive Technologies report discusses best practices for collecting, using, and transferring body-related data between entities.
#new: @futureofprivacy Release of ‘Risk Framework for Body-Related Data in Immersive Technologies’ written by the author @spibackjameson & @Daniel Beric.
This analysis helps ensure that organizations are handling body-related data safely and responsibly. https://t.co/FC1VOsaAFe
— Future of Privacy Forum (@futureofprivacy) December 12, 2023
Organizations, businesses, and individuals can integrate FPF’s observations into recommendations and foundations for promoting safe and responsible extended reality (XR) policies. This is relevant for companies that require large amounts of biometric data in immersive technologies.
Those following the report’s guidance will also be encouraged to document the reasons and methodologies for processing biometric data, ensure compliance with laws and standards, assess risks related to privacy and safety, and address ethical considerations when collecting data from devices. You can apply the framework to write .
This framework applies not only to XR-related organizations, but also to all institutions utilizing technologies that rely on biometric processing.
Jameson Spivack, Senior Policy Analyst, Immersive Technologiesand Daniel Berrick, Policy Advisorco-authored the report.
Your data: processed with care
To understand how personal data is processed, organizations must identify potential privacy risks, ensure compliance with the law, and implement best practices to enhance safety and privacy, FPF explained.
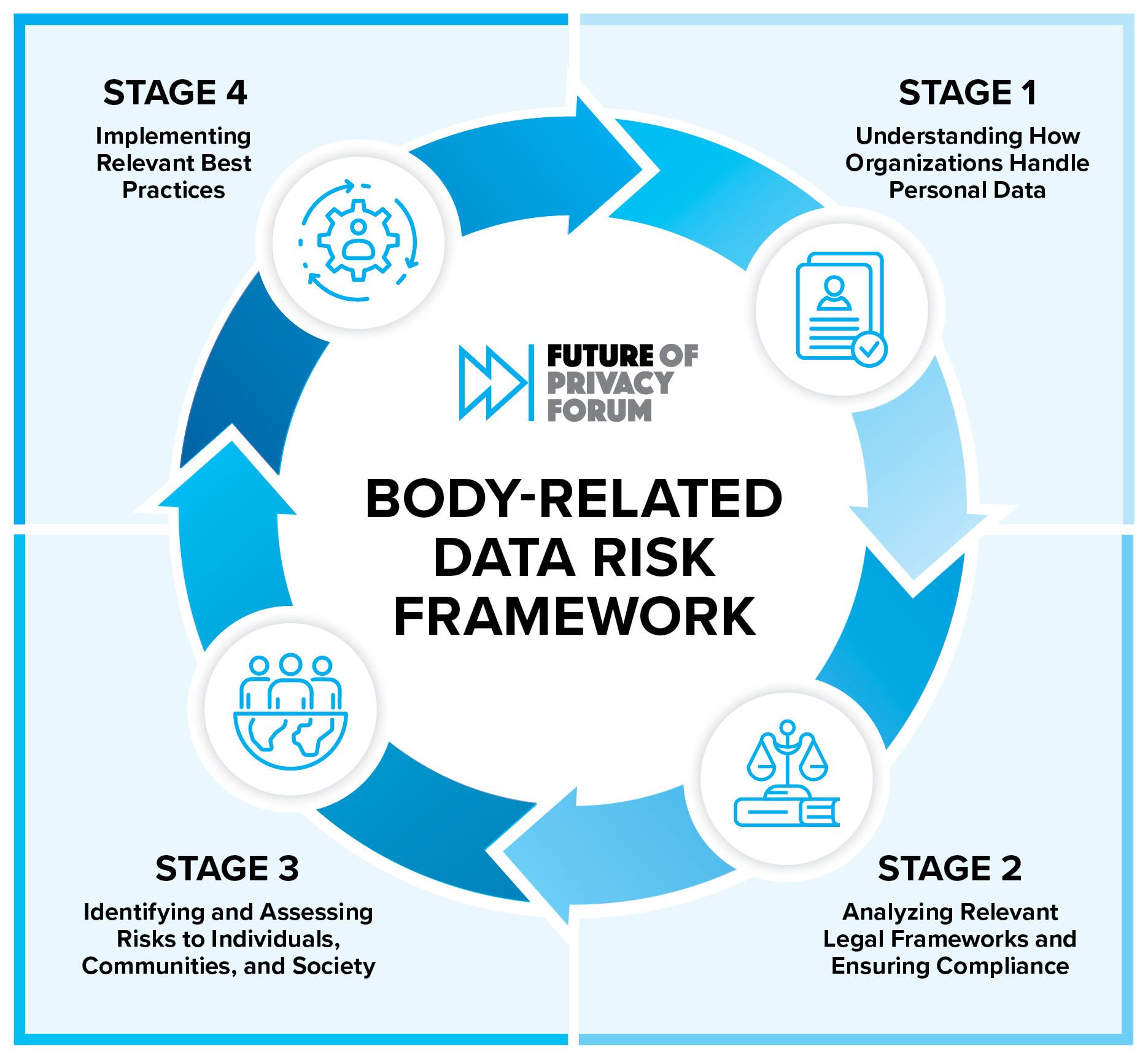
According to Level 1 The framework allows organizations to:
- Create a data map that outlines data practices linked to biometric information
- Document use of data and practices
- Identify relevant stakeholders (direct and third parties) affected by your organization’s data practices.
Companies analyze the applicable legal framework. Step 2 Ensure compliance. This includes companies that collect, use, or transmit “data about the body” that is subject to U.S. privacy laws.
To comply, the framework recommends that organizations “understand the individual rights and business obligations” that apply to “existing comprehensive and sector-specific privacy laws.”
Organizations should also analyze new laws and regulations and how they will impact “body-based data practices.”
in Step 3, companies, organizations and institutions must identify and assess risks to others. This includes the individuals, communities and societies they serve, he explained.
The report said privacy risks and harms can arise from data that is “used or processed in a particular way or transmitted to particular parties.”
Compliance with the law alone “may not be sufficient to mitigate risks,” he added.
To maximize safety, companies can follow several steps to protect their data, including proactively identifying and reducing risks associated with their data practices.
This includes impacts to:
-
- identifiability
- Used to make key decisions
- sensitivity
- Partners and other third party groups
- possibility of inference
- data retention
- Data accuracy and bias
- User expectations and understanding
After assessing a group’s data use policy, the organization can assess the fairness and ethics of its data practices based on the risks identified, it explained.
Finally, the FPF framework recommended best practice implementation. Step 4This includes a variety of legal, technical and policy safeguards available to organizations.
It added that this will help organizations “comply with laws and regulations, minimize privacy risks, and ensure that immersive technologies are used fairly, ethically and responsibly.”
The framework encourages organizations to intentionally implement best practices by comprehensively “addressing all parts of the data lifecycle and addressing all associated risks.”
Organizations can also implement best practices collaboratively, using best practices “developed in consultation with cross-disciplinary teams within the organization.”
This includes legal product, engineering, trust, safety and privacy stakeholders.
Organizations can protect their data by:
- Data localization and processing on devices and storage
- Minimize data footprint
- Third Party Management Regulation or Enforcement
- Providing Meaningful Notice and Consent
- Preserve data integrity
- Provides user control
- Integration of privacy-enhancing technologies
These best practices allow organizations to evaluate best practices and adjust them appropriately into a coherent strategy. After that, we were able to continuously evaluate best practices to maintain efficiency.
EU pushes for artificial intelligence (AI) law
The news comes shortly after the EU pushed for AI laws that FPF countries say will have “far-reaching extraterritorial implications.”
The bill, currently being negotiated with member states, aims to protect citizens from harmful and unethical use of AI-based solutions.
An EU political agreement has been reached. #AI Act, which will have far-reaching extraterritorial implications. If you would like to gain insight into the key legal implications of the regulations, @kate_deme In-depth FPF training will be held tomorrow at 11 AM ET.
: https://t.co/weVgDdsvRh— Future of Privacy Forum (@futureofprivacy) December 11, 2023
The organization provides guidance, expertise and training for businesses as they prepare to implement the law. This marks one of the biggest changes to data privacy policies since the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was introduced in May 2016.
The European Commission has said it wants to “regulate artificial intelligence (AI)” to ensure improved conditions for the use and rollout of the technology.
The statement said:
“In April 2021, the European Commission proposed the first EU regulatory framework for AI. AI systems that can be used for various applications are analyzed and classified according to the risks they pose to users. Different levels of risk imply different degrees of regulation. Once approved, this will be the world’s first rule on AI.”
The goal is to approve the bill by the end of this year, according to the committee.
Biden-Harris Executive Order on AI
The Biden-Harris administration implemented an executive order on AI regulation in late October. The government’s Executive Order on Safe and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence aims to protect citizens around the world from the harmful effects of AI programs.
Companies, organizations and experts must comply with new regulations for “developers of the most powerful AI systems” to share safety assessments with the U.S. government.
FPF said the plan was “incredibly comprehensive” and offered a “whole-of-government approach with impact beyond government agencies”.
This was followed up in an official statement.
“While the executive order is focused on the government’s use of AI, the impact on the private sector will be enormous due to its broad requirements for government vendors, monitoring workers, prioritizing education and housing, and developing standards for conducting risk assessments and mitigating bias. It will. , investment in technology to enhance personal information protection, etc.”
The statement also urged lawmakers to enact “bipartisan privacy legislation.” This was “the most important precursor to protecting AI affecting vulnerable populations.”
UK holds AI Security Summit
The UK also hosted an AI Security Summit at the iconic Bletchley Park, where world-renowned scientist Alan Turing cracked the Nazis’ World War II Enigma code.
The world-class event brought together some of the industry’s leading experts, executives, companies and organizations to outline safeguards for AI regulation.
These include US, UK, EU and UN governments, the Alan Turing Institute, The Future of Life Institute, Tesla, OpenAI and others. The group discussed ways to build a shared understanding of the risks of AI, collaborate on best practices, and develop a framework for AI safety research.
The fight for data rights
The news comes as several organizations form new alliances to address ongoing concerns about the use of virtual, augmented and mixed reality (VR/AR/MR), AI and other emerging technologies.
For example, Meta Platforms and IBM have launched a large-scale alliance to help develop best practices for artificial intelligence, biometric data, and create a regulatory framework for technology companies around the world.
The Global AI Alliance hosts more than 30 organizations, companies, and individuals from across the global technology community, including tech giants like AMD, HuggingFace, CERN, the Linux Foundation, and more.
Additionally, organizations such as the Washington DC-based XR Association, Europe’s XR4Europe alliance, and the globally recognized Metaverse Standards Forum and Gatherverse have contributed enormously to implementing best practices for those involved in building the future of the space. technology.

