Victoria d’Este
Posted: December 20, 2024 9:56 AM Updated: December 20, 2024 9:56 AM

Correction and fact check date: December 20, 2024, 9:56 AM
briefly
In 2024, North Korean hackers stole $2.2 billion worth of cryptocurrency assets, posing a growing threat to global security and the cryptocurrency industry.

The cryptocurrency industry took a tragic turn in 2024 when hackers took advantage of a flaw to steal $2.2 billion worth of digital assets. Among them, North Korean hackers were the most powerful, stealing as much as $1.3 billion. The growing threat to cryptocurrency businesses and global security is highlighted by the fact that the value stolen by North Korea-related entities has increased by 102.88% since 2023, according to Chainalytics.
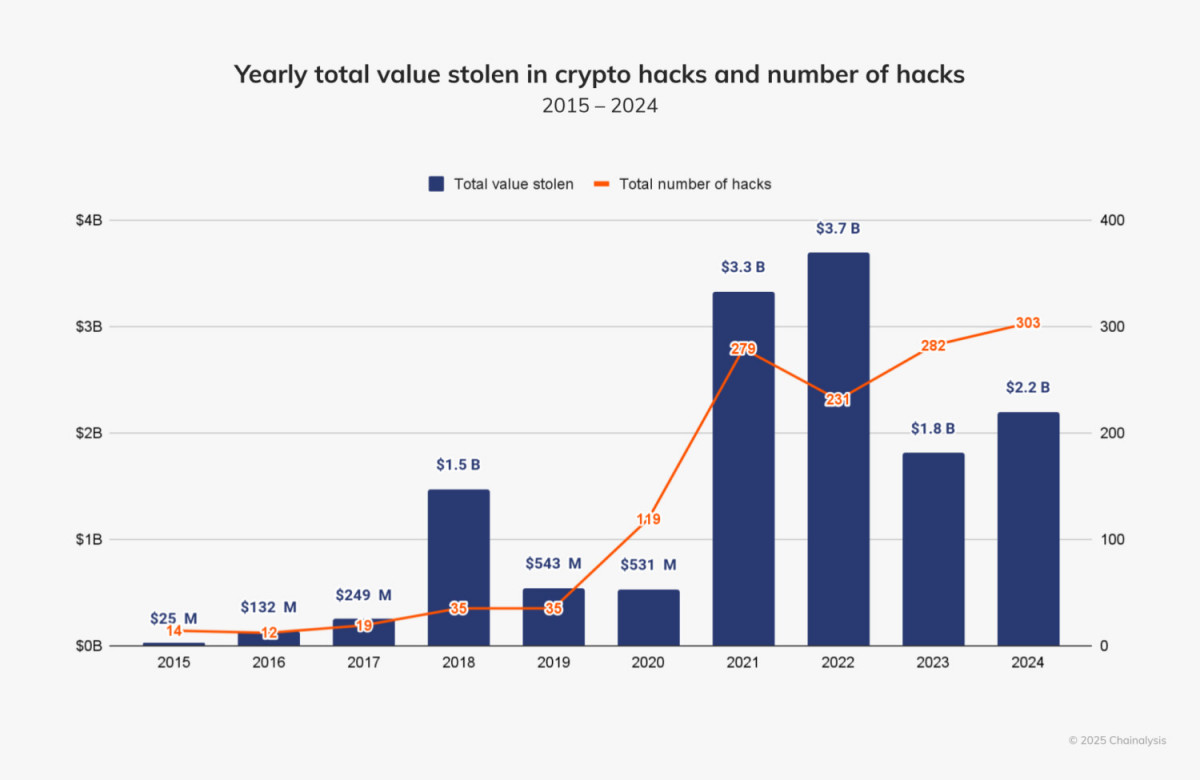
Photo: Chainalysis
Digital theft is on the rise
The sector has always struggled with cryptocurrency theft and has seen historically large amounts of money stolen over the years. As the frequency and intensity of hacking attacks increases, the total amount of hacking in 2024 increased by more than 21% compared to the previous year. The number of reported breaches increased from 282 in 2023 to a total of 303, highlighting the continued vulnerability of the industry.
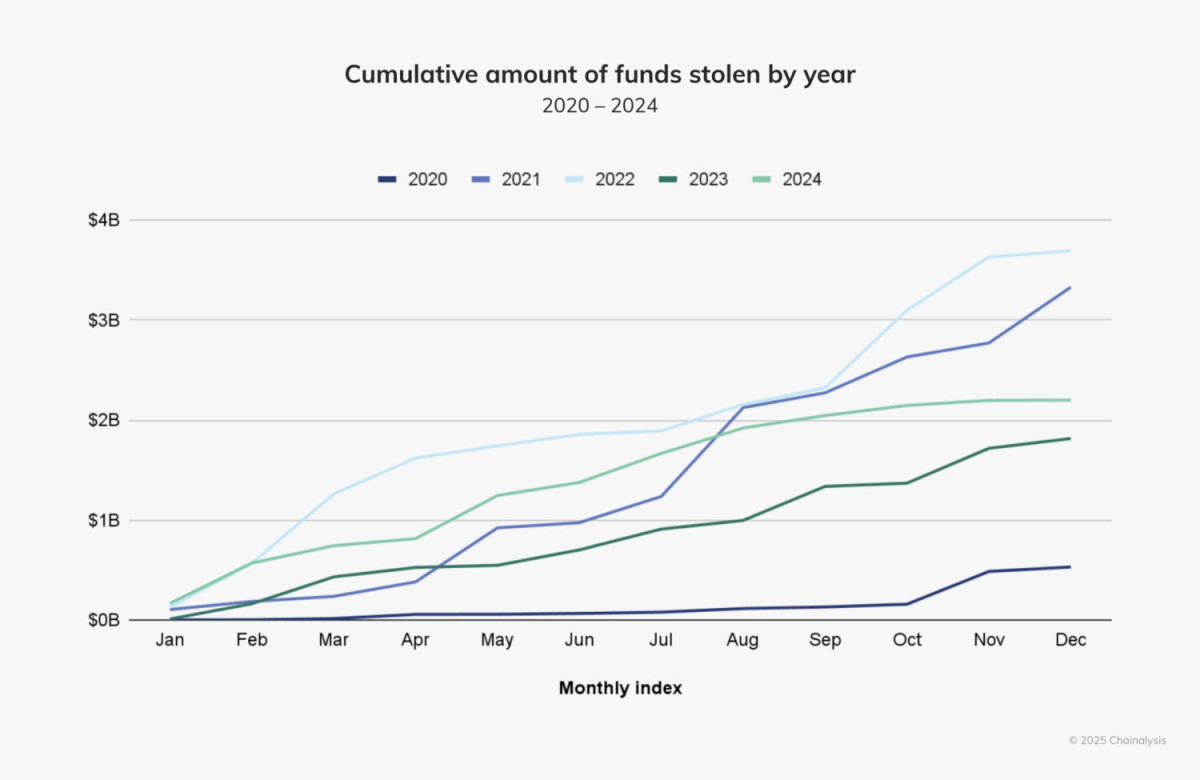
Photo: Chainalysis
In 2024, hacking activity took a different direction. From January to July, cryptocurrency theft totaled $1.58 billion, an 84.4% increase compared to the same period in 2023. Initially, analysts thought 2024 could match the record years of 2021 and 2022. Year. However, as hacking cases have decreased significantly since the middle of this year, the possibility of external influence has also been raised.
Shifting Goals: Centralized Platforms and DeFi
Hackers have historically targeted decentralized financial networks because of their rapid development cycles and sometimes inadequate security mechanisms. As of early 2024, the majority of stolen assets belonged to DeFi. Nonetheless, there was a noticeable change in the second and third quarters of this year as centralized systems took the brunt of attacks.
This trend can be seen in two major breaches: the $234.9 million loss of WazirX in July and the $350 million DMM Bitcoin hack in May. These incidents highlight the weaknesses of centralized services, especially when it comes to private key management. Private key compromise was the most frequent attack vector in 2024, accounting for 43.8% of all cryptocurrency theft.
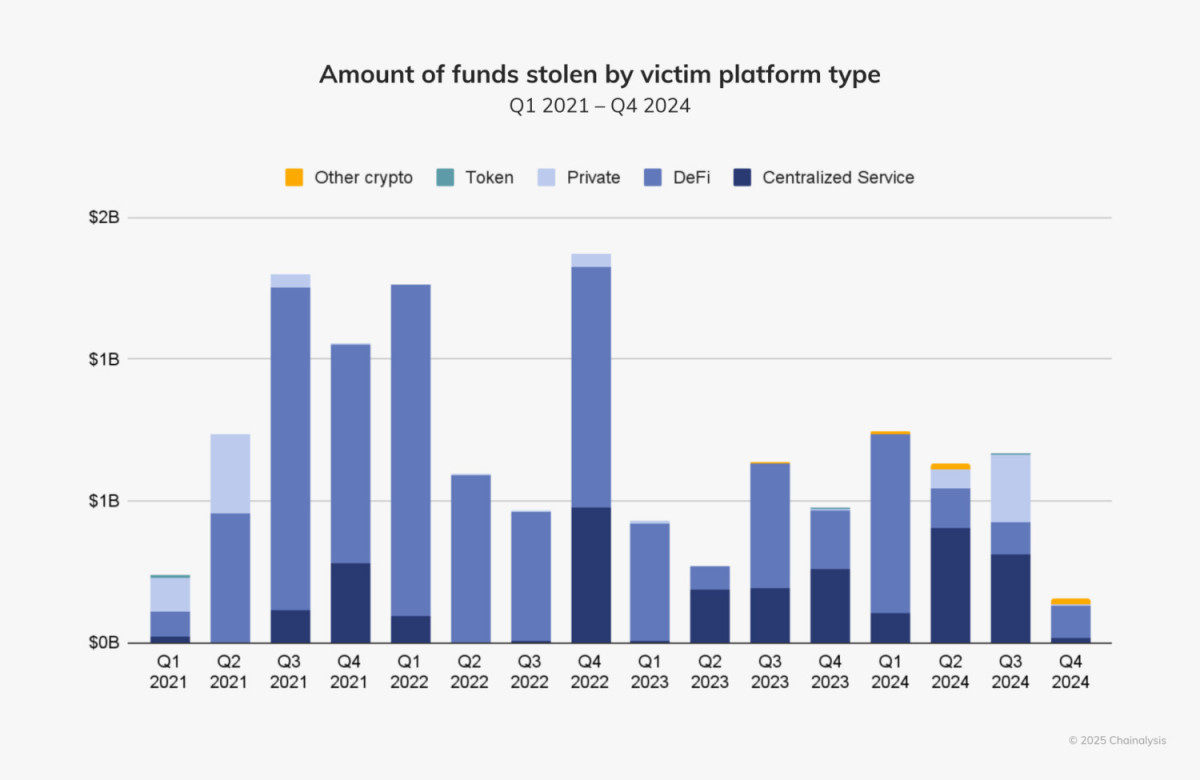
Photo: Chainalysis
An essential part of the security is the private key, which provides access to the user’s money. The DMM Bitcoin hack shows that any compromise can lead to disastrous results. In addition to causing financial losses, the exchange failed to adequately protect private keys and was ultimately shut down later that year.
Main participant in cryptocurrency hacking – North Korea
Widespread cryptocurrency theft has been linked to North Korean hackers, it has been revealed. These are the most common actors in the space in 2024, accounting for 61% of total filming dollars. The $1.3 billion lost in 47 attacks is a significant increase over the $660.5 million lost in 20 hacks in 2023. North Korea’s reliance on cryptocurrency theft to finance its weapons program and evade international sanctions is reflected in this surge in activity.
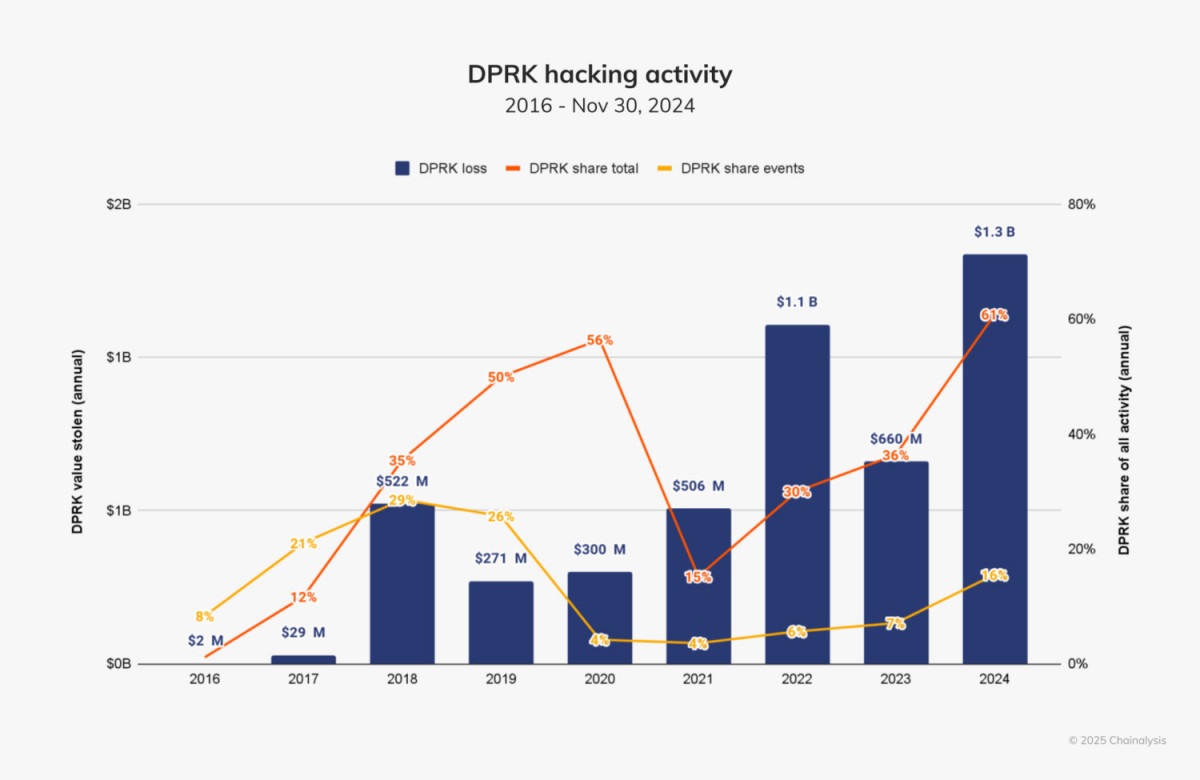
Photo: Chainalysis
North Korean hackers have developed increasingly complex strategies. They conducted large-scale attacks more frequently in 2024, more often targeting amounts greater than $50 million than in previous years. They also expanded their scope to include smaller scale hacks, targeting amounts as small as $10,000.
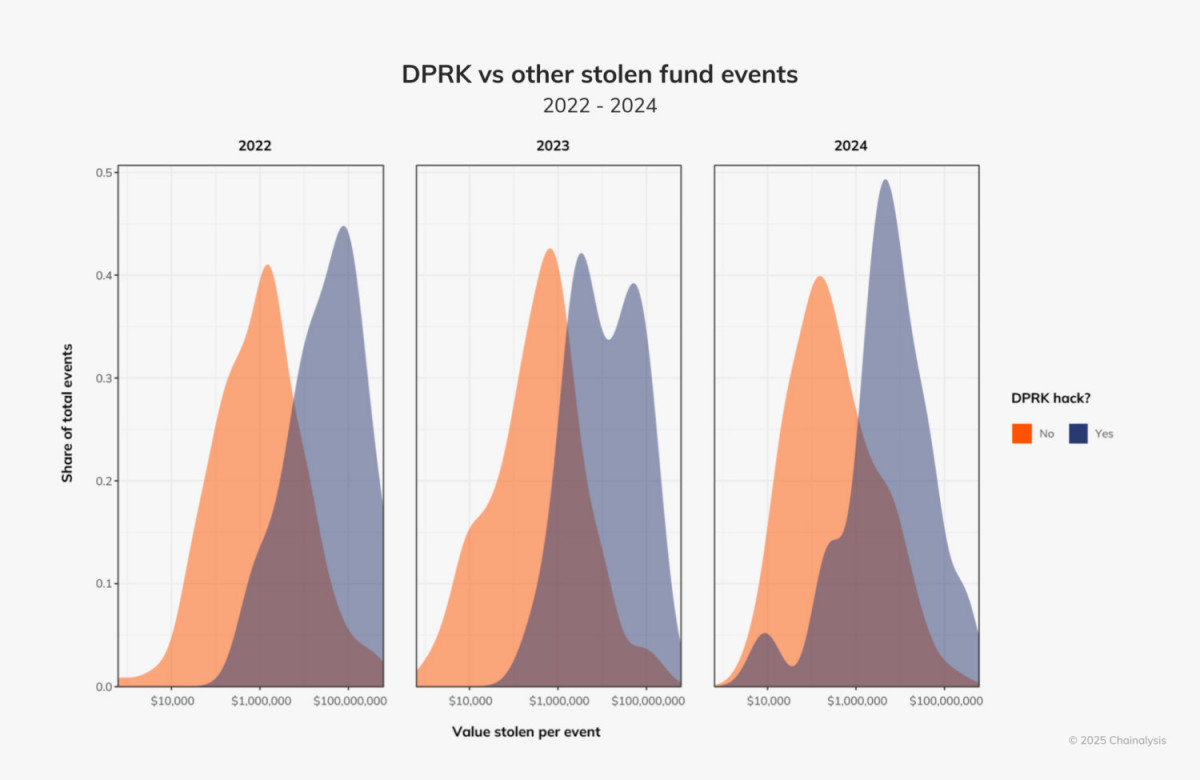
Photo: Chainalysis
Cyber espionage and personnel infiltration
North Korean IT experts infiltrating cryptocurrency companies is a development problem. To gain access to sensitive networks, these agents use virtual identities, third-party agents, and remote employability. In one well-known case, 14 North Koreans were accused of using this method to steal $88 million. To prevent such breaches, these strategies emphasize the need for rigorous employee screening and strong cybersecurity procedures.
North Korea’s cyber activity increased sharply in the first half of 2024, but decreased significantly after July. The geopolitical event of the summit between North Korean leader Kim Jong-un and Russian President Vladimir Putin coincided with this decline. North Korea’s hacking activities appeared to show changes after the meeting, with the value of daily stolen cash decreasing by 53.73%. However, over the same period, hacking activity by non-North Koreans increased slightly.
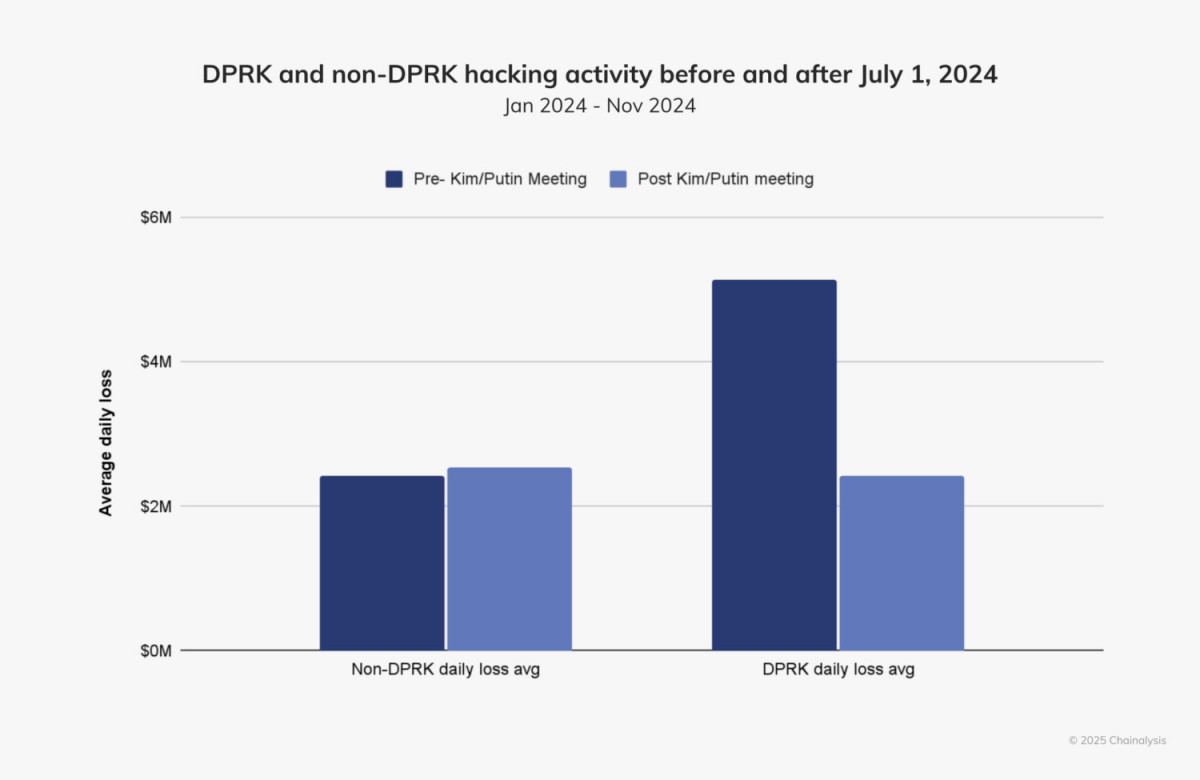
Photo: Chainalysis
The cause of this worsening is not yet known. It is possible that North Korea transferred funds to support its military partnership with Russia, including sending ballistic missiles and personnel to Ukraine. On the other hand, these delays may also be the result of a strategic shift in North Korea’s cyber activities.
DMM Bitcoin Breach Case Study
One of the most significant events of 2024 was the $305 million DMM Bitcoin breach. North Korean hackers stole 4,502.9 bitcoins by exploiting a loophole in the exchange system that allowed them to obtain private keys without permission. After being laundered through a mixing service, the stolen money was transferred to a platform linked to Huione Group, a cybercrime affiliate based in Cambodia.
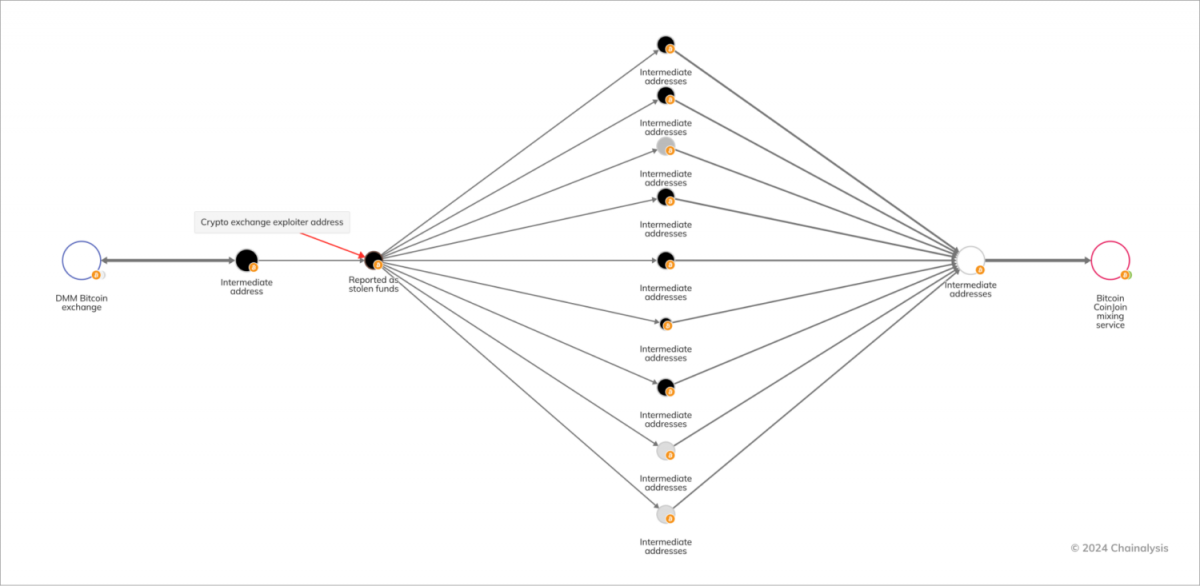
Photo: Chainalysis
This violation has serious repercussions. With the goal of completing the transition by 2025, DMM Bitcoin has ceased operations and transferred its assets to SBI VC Trade. This incident highlights the need for proactive defense against such attacks and the disastrous impact of inadequate security measures.
Predictive Models and the Future of Cryptocurrency Security
The development of predictive technologies offers the potential to combat cryptocurrency theft. Chainalytic’s acquisition of Web3 security company Hexagate is a big step toward proactive threat detection. Real-time blockchain activity analysis is performed through Hexagate’s machine learning algorithms, which uncover suspicious trends and possible attacks before they occur.
For example, two days before the attack, Hexagate discovered a $20 million contract related to the UwU Lend vulnerability. Although the link to the final attack was not immediately apparent, the potential of these technologies to prevent financial loss through early identification was demonstrated.
Despite these advances, the effectiveness of predictive models depends on how well they are integrated into current security systems. To ensure that such risks are eliminated before they become more serious, protocols must be equipped with the tools necessary to respond to early warnings.
The surge in cryptocurrency theft in 2024 highlights how urgently improved security measures are needed. Addressing the changing threat landscape requires a collaborative strategy combining regulators, law enforcement, and industry stakeholders. A thorough security plan should include robust private key management, sophisticated tracking capabilities, and real-time monitoring.
disclaimer
In accordance with the Trust Project Guidelines, the information provided on these pages is not intended and should not be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial or any other form of advice. It is important to invest only what you can afford to lose and, when in doubt, seek independent financial advice. We recommend that you refer to the Terms of Use and help and support pages provided by the publisher or advertiser for more information. Although MetaversePost is committed to accurate and unbiased reporting, market conditions may change without notice.
About the author
Victoria is a writer covering a variety of technology topics, including Web3.0, AI, and cryptocurrency. Her extensive experience allows her to write insightful articles for a wider audience.
more articles

Victoria d’Este

Victoria is a writer covering a variety of technology topics, including Web3.0, AI, and cryptocurrency. Her extensive experience allows her to write insightful articles for a wider audience.


